Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are essential components in almost every electronic device we use today. From smartphones to complex industrial machinery, PCBs provide the foundation for the electrical connections necessary for the operation of electronic components. This guide explores the various aspects of PCBs, including their structure, manufacturing processes, and applications.
A typical PCB consists of a non-conductive substrate, usually made from fiberglass, with conductive copper pathways printed onto its surface. These pathways connect various electronic components, including resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits. The layout of these components and connections is crucial for the performance and reliability of the electronic device.
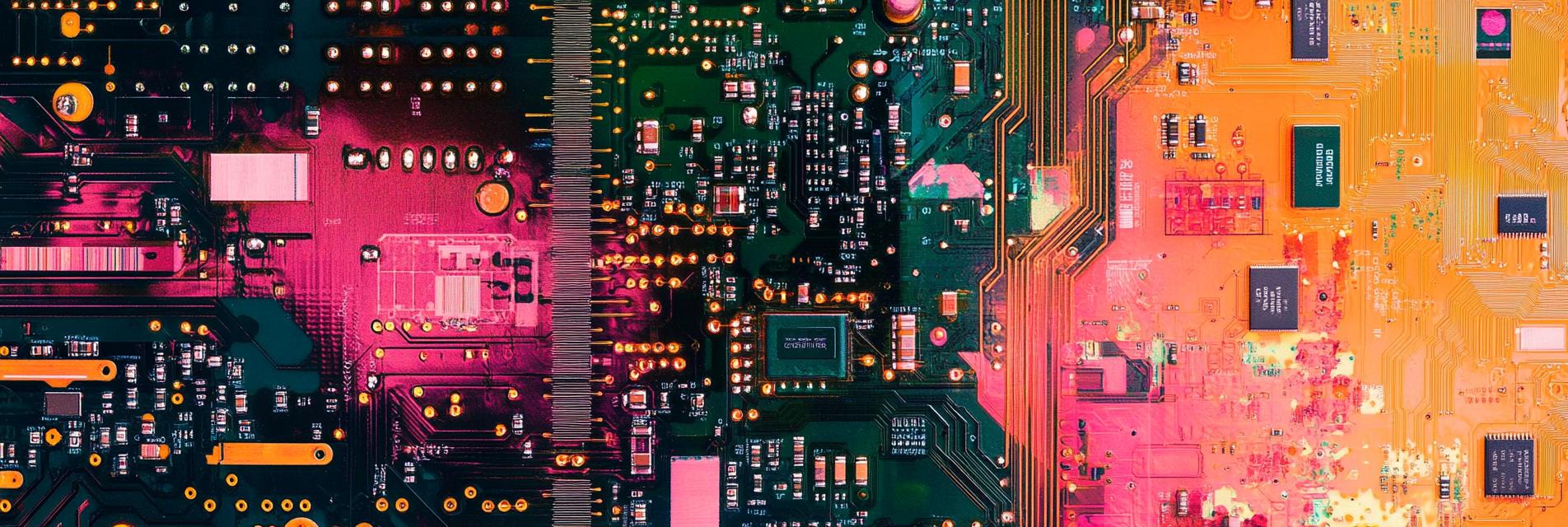
The manufacturing of PCBs can vary depending on their complexity and specifications. Generally, the process involves several key steps, including:
PCBs are used across various industries, including consumer electronics, telecommunications, and automotive sectors. Their versatility allows for a wide range of applications:
Understanding printed circuit boards is crucial for anyone involved in electronics, whether as a designer, engineer, or technician. As technology evolves, the demand for advanced and efficient PCBs will continue to grow, further enhancing their importance in modern electronics.
